Thermoacoustics
Thermoacoustic instabilities constitute a major recurring problem to be dealt with when developing combustion chambers (small and large scale boilers, combustion-based heating devices, aeroengines, gas turbines for power generation or rocket engines). It is induced by the coupling between flames and combustion chamber acoustics. These constructive nonlinear acoustic-flame interactions can yield high amplitude dynamic pressure limit cycles, which reduce the lifetime of the hot gas path parts, or in the worst case, destroy them during a sudden catastrophic event. The only way to avoid them is to narrow the combustor operating window to regions where the acoustic level is acceptable.
A strong research effort aims at understanding the fundamental phenomena associated with thermoacoustic instabilities: Investigations of the nonlinear flame dynamics when it is submitted to acoustic perturbations, experimental and numerical flame response identification and modeling, Large Eddy Simulations of the instabilities, modeling of the thermoacoustic coupling in the chamber, development of passive damping systems, analysis of the stochastic aspects of the coupling, the combustion noise, the azimuthal modes in annular combustion systems...
Acoustic pressure drives burner aerodynamics and yields coherent fluctuations of velocity and equivalence ratio upstream of the flame. In addition the highly turbulent flow field produces stochastic fluctuations of these quantities. Through combustion process, the sum of these perturbations turns into coherent and stochastic heat release rate fluctuations, also accompanied with entropy waves being propagated downstream at mean flow velocity. The time derivative of the heat release rate is a source term in the acoustic wave equation. Therefore such system can exhibit large amplitude self-sustained thermoacoustic oscillations due to the constructive 2-ways interactions between flame and chamber's acoustics. In this context, our research aims at better understanding and controlling this type of combustion instabilities.
Publications

Acoustic amplification potential and thermoacoustic instabilities of staged multi-jet hydrogen flames
K. Moon, N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Volume 41, 2025
One of the most challenging problems in the development of hydrogen gas turbine engines is predicting and mitigating self-excited combustion instabilities. In this experimental study, we employ a fuel staging method, which is implemented by splitting the total hydrogen mass flowrate into two separate fuel circuits for the transition of combustion modes between fully-premixed (FP) and technically-premixed (TP) conditions, to suppress the thermoacoustic oscillations, fundamentally through interference mechanisms of convective disturbances. […]


Quantifying uncertainties in the input–output identification of Flame Transfer Functions
J.F. Radack, B. Dharmaputra, B. Schuermans, N. Noiray
Combustion and Flame, vol. 281, November 2025
The FIR model of a flame subject to acoustic forcing can be identified from numerical simulations. It is often subsequently used to obtain the frequency domain Flame Transfer Function (FTF). We provide the exact mathematical connection between the models uncertainty in the time and frequency domain, and give the sampling distributions for the gain and phase of the transfer function. […]


Identification of instantaneous flame transfer functions
J.F. Radack, B. Schuermans, N. Noiray
Combustion and Flame, vol. 279, September 2025
Most existing system identification methods are designed for time-invariant systems. However, for many practical applications, data collection over a wide range of parameters under stationary conditions is either infeasible or costly. To address this limitation, we propose a time-domain, nonparametric methodology for linear, time-varying (LTV) systems, extending the classical paradigm of impulse response function estimation from broadband data using least-squares regression. We introduce the time-varying impulse response function (TV-IRF), which uniquely characterizes the dynamic behavior of LTV systems, and represent it as a series expansion over an orthonormal basis. […]

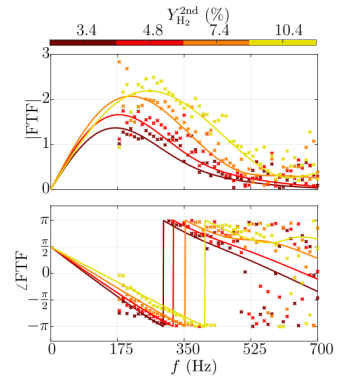
Flame transfer function measurement of a sequential combustor fuelled with natural gas and hydrogen.
B. Dharmaputra, P. Nagpure, M. Impagnatiello, N. Noiray
Combustion and Flame, vol. 274, pp. 113972, 2025
The flame transfer function (FTF) relates acoustic perturbations and the coherent heat release rate response. This frequency-dependent function governs the thermoacoustic stability of a combustor. The FTF measurement is therefore of great interest for predicting the stability of the practical combustor connected to the engine’s compressor and turbine. So far, the FTFs of the second stage of constant pressure sequential combustors (CPSC) have only been obtained from numerical simulations. In this study, second-stage FTFs are measured experimentally. [...]

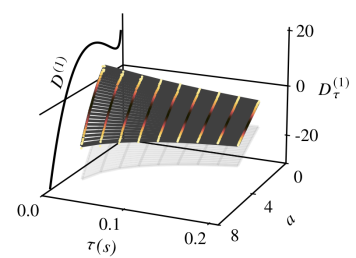
A deep operator network for Bayesian parameter identification of self-oscillators
T. Sugandi, B. Dharmaputra, and N. Noiray
Data-Centric Engineering, Vol. 5, 2024
Many physical systems exhibit limit-cycle oscillations that can typically be modeled as stochastically driven self-oscillators. In this work, we focus on a self-oscillator model where the nonlinearity is on the damping term. In various applications, it is crucial to determine the nonlinear damping term and the noise intensity of the driving force. This article presents a novel approach that employs a deep operator network (DeepONet) for parameter identification of self-oscillators. [...]

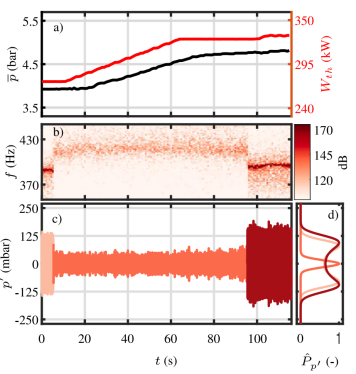
Plasma assisted thermoacoustic stabilization of a transiently operated sequential combustor at high pressure
B.Dharmaputra, S. Shcherbanev, and N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol. 40, 2023
This study demonstrates the stabilization of a thermoacoustic instability in a sequential combustor at elevated pressure conditions using Nanosecond Repetitively Pulsed Discharges (NRPD). Sequential combustors operating at constant pressure offer several advantages over their conventional counterparts, including increased fuel flexibility and a wider operating range. In this work, we investigate the control of thermoacoustic instabilities with NRPD up to 6 bar, in both stationary and transient modes of operation. [...]

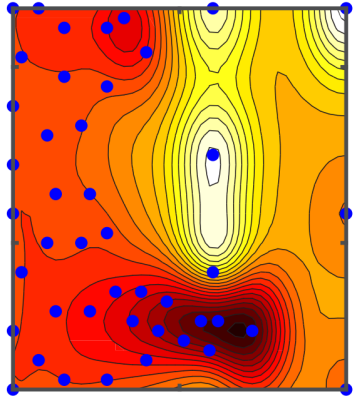
BOATS: Bayesian Optimization for Active control of ThermoacousticS
B.Dharmaputra, P. Reckinger, B. Schuermans, and N. Noiray
Journal of Sound and Vibration, Vol. 582, 2024
This investigation presents novel adaptive control algorithms specifically designed to address and mitigate thermoacoustic instabilities. Gas turbines are limited in their operational range due to thermoacoustic instability. Two control strategies are available to alleviate this issue: active and passive. Active control strategies have a wider flexibility than passive control strategies because they can adapt to the operating conditions of the gas turbine. [...]

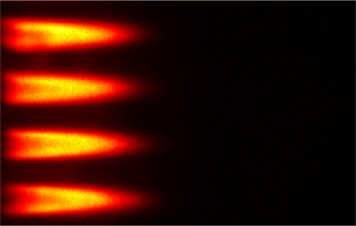
Transfer functions of lean fully- and technically-premixed jet-stabilized turbulent hydrogen flames
K. Moon, R. Martin, B. Schuermans, and N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol. 40, 2024
Understanding the response of multi-jet turbulent hydrogen-air flames to acoustic forcing is key for the development of future carbon-neutral gas turbine combustors. In this paper, we present flame transfer functions (FTFs) deduced from burner and flame transfer matrices obtained with acoustic measurements for fully-premixed (FP) and technically-premixed (TP) conditions, in conjunction with their analytical models. [...]

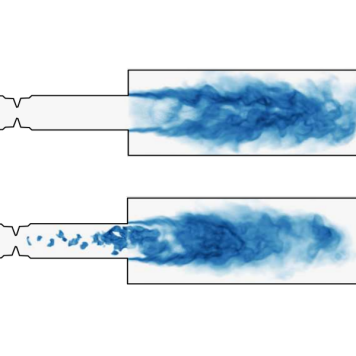
Acoustic scattering of a sequential combustor controlled with non-equilibrium plasma: a numerical study
M.Impagnatiello, Q.Malé, and N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol. 40, 2023
The impact of Nanosecond Repetitively Pulsed Discharges (NRPDs) on the acoustic scattering properties of the second stage of a Constant Pressure Sequential Combustor (CPSC) is investigated using Large Eddy Simulations (LESs) with state-of-the-art plasma modeling, combined with methods from System Identification. The results demonstrate that plasma-generated ignition kernels significantly mitigate the system's acoustic power amplification by inducing heat release fluctuations that are out of phase with local pressure fluctuations. [...]


Thermoacoustic stabilization of a sequential combustor with ultra-low-power nanosecond repetitively pulsed discharges
B. Dharmaputra, S. Shcherbanev, B. Schuermans and N. Noiray
Combustion and Flame, Volume 258, 2023
This study demonstrates successful suppression of instabilities using NRPD in a lab-scale atmospheric sequential combustor, even at low plasma power (1.1 W, about 1.5e-3 percent of thermal power of 73.4 kW). We also examine the effect of pulse repetition frequency and plasma generator voltage on NO emissions and the sequential flame topology. Notably, higher plasma power can further enhance suppression, albeit with a slight increase in NO emissions. Intriguingly, specific plasma parameter combinations can excite another acoustic mode, necessitating further exploration for optimized control. This pioneering study highlights the potential of ultra-low-power plasma-based thermoacoustic control in sequential combustors, paving the way for enhanced stability and performance. [...]

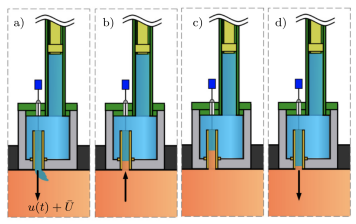
Failure of thermoacoustic instability control due to periodic hot gas ingestion in Helmholtz dampers
L. Miniero, G. A. Mensah, C. Bourquard and N. Noiray
Journal of Sound and Vibration, Vol. 548, 2023
The periodic ingestion of the combustion chamber hot gas in the resonant cavity of Helmholtz dampers can be a serious issue, if not considered in the design phase of these devices. This study presents experimental and theoretical investigations of that problem. A physics-based model is derived with a few empirical parameters, calibrated with data which were collected from an experimental setup comprising a tunable Helmholtz damper connected to a combustor operated at atmospheric pressure. [...]

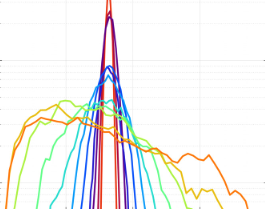
Symmetry Breaking in an Experimental Annular Combustor Model With Deterministic Electroacoustic Feedback and Stochastic Forcing
S. C. Humbert, A. Orchini, C. O. Paschereit and N. Noiray
Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, Vol. 145, 2023
In this study, we use an annular combustor experimental model with electroacoustic feedback to investigate systematically the effect of stochastic forcing and nonuniform flame response distribution on azimuthal thermoacoustic modes. We break the symmetry of a nominally degenerate mode [...]
external page View at publisher

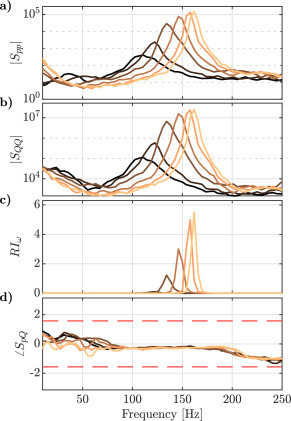
The Rayleigh integral is always positive in steadily operated combustors
B. Schuermans, J. Moeck, A. Blondé, B. Dharmaputra and N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol. 39, 2022
The Rayleigh index has been used for decades by a large number of researchers as an indicator to determine if a flame is driving or damping thermoacoustic interaction mechanisms. It is commonly assumed in literature that the sign of the Rayleigh index from steady state data can be used to determine if the thermoacoustic feedback loop is stabilizing or destabilizing. However, we show in this paper that under fairly general conditions, a correctly measured Rayleigh index is always positive if evaluated from statistically stationary data. [...]
external page View at publisher

Entropy transfer function measurement with tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy
B. Dharmaputra, S. Shcherbanev, A. Blondé, B. Schuermans and N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol. 39, 2022
Tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) with wavelength modulation spectroscopy (WMS) has been widely applied to measure the gas temperature and species concentration in combustion environments. In this work, we show the capability of TDLAS in measuring the coherent temperature fluctuations of a turbulent swirled flame. Two distributed feedback grating (DFB) lasers are used to probe the H2O absorption transitions near 7185.59 cm−1 and 6806.03 cm−1. [...]
external page View at publisher

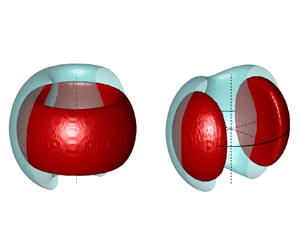
Spontaneous and explicit symmetry breaking of thermoacoustic eigenmodes in imperfect annular geometries
T. Indlekofer, A. Faure-Beaulieu, J. Dawson and N. Noiray
Journal of Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 944, 2022
This article deals with the symmetry breaking of azimuthal thermoacoustic modes in annular combustors. Using a nominally symmetric annular combustor, we present experimental evidence of a predicted spontaneous reflectional symmetry breaking, and also an unexpected explicit rotational symmetry breaking in the neighbourhood of the Hopf bifurcation which separates linearly stable azimuthal thermoacoustic modes from self-oscillating modes. [...]

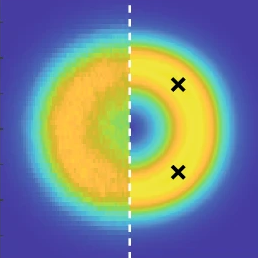
Steady-state statistics, emergent patterns and intermittent energy transfer in a ring of oscillators
T. Pedergnana and N. Noiray
Nonlinear Dynamics, Vol. 108, 2022
Networks of coupled nonlinear oscillators model a broad class of physical, chemical and biological systems. Understanding emergent patterns in such networks is an ongoing effort with profound implications for different fields. In this work, we analytically and numerically study a symmetric ring of N coupled self-oscillators of van der Pol type under external stochastic forcing. [...]


Coupling-induced instability in a ring of thermoacoustic oscillators
T. Pedergnana and N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Royal Society A, Vol. 478, 2022
Thermoacoustic instabilities in can-annular combus-tors of stationary gas turbines lead to unstable Bloch modes which appear as rotating acoustic pressure waves along the turbine annulus. The multiscale, multiphysical nature of the full problem makes a detailed analysis challenging. In this work, we derive a low-order, coupled oscillators model of an idealized can-annular combustor. [...]

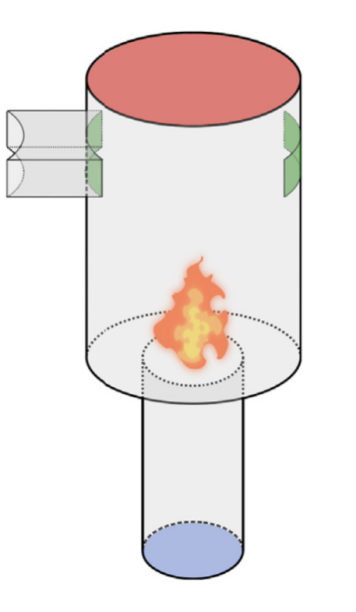
Reduced-order modelling of thermoacoustic instabilities in can-annular combustors
A. Orchini, T. Pedergnana, P. E. Buschmann, J. P. Moeck and N. Noiray
Journal of Sound and Vibration, Vol. 526, 2022
Thermoacoustic instabilities in stationary gas turbines may cause high-amplitude limit cycles, leading to damaged components and costly down-time. To better understand the physical origin of such instabilities in a can-annular combustor configuration, we study the properties of the spectrum of a reduced-order can-annular thermoacoustic system. [...]

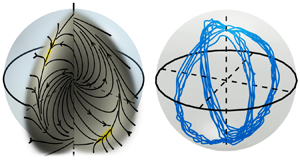
Imperfect symmetry of real annular combustors: beating thermoacoustic modes and heteroclinic orbits
A. Faure-Beaulieu, T. Indlekofer, J. R. Dawson, N. Noiray
Journal of Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 925, 2021
In jet engines and gas turbines, the annular shape of the combustion chamber allows the appearance of self-oscillating azimuthal thermoacoustic modes. We report experimental evidence of a new type of modal dynamics characterised by periodic switching of the spinning direction and develop a theoretical model that fully reproduces this phenomenon and explains the underlying mechanisms. [...]


Low order modelling of thermoacoustic instabilities and intermittency: Flame response delay and nonlinearity
G. Bonciolini, A. Faure-Beaulieu, C. Bourquard, N. Noiray
Combustion and Flame, Vol. 226, 2021
This paper investigates the simplifying assumptions used for deriving low order models of thermoacoustic instabilities and thermoacoustic intermittency in turbulent combustor. These models consists in self-sustained oscillators subject to parametric and additive stochastic forcing. The main aspects of the thermoacoustic dynamics investigated in the present work are the phase between acoustic pressure and heat release rate oscillations, and the nonlinearity ruling the saturation of the flame response. [...]

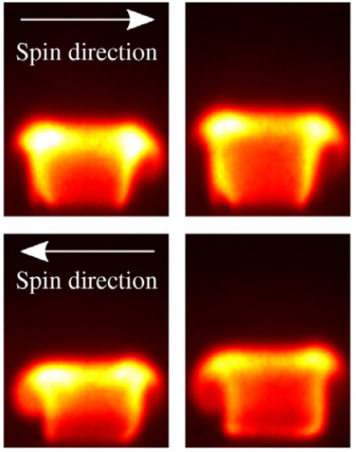
The effect of dynamic operating conditions on the thermoacoustic response of hydrogen rich flames in an annular combustor
T. Indlekofer, A. Faure-Beaulieu, N. Noiray and J. Dawson
Combustion and Flame, Vol. 223, 2021
Self-excited thermoacoustic instabilities in symmetric annular combustion chambers typically give rise to spinning, standing and mixed azimuthal modes which are time-varying in nature and occur in a highly noisy environment due to turbulent combustion. We investigate the effect of linear ramps of increasing and decreasing equivalence ratio on the operating limits and thermoacoustic dynamics, from near lean blow-off to near flashback, in a laboratory scale annular combustor. [...]


Experiments and low-order modelling of intermittent transitions between clockwise and anticlockwise spinning thermoacoustic modes in annular combustors
A. Faure-Beaulieu, T. Indlekofer, J. R. Dawson, N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol. 38, 2021
Annular combustion chambers of gas turbines and aircraft engines are subject to unstable azimuthal thermoacoustic modes leading to high amplitude acoustic waves propagating in the azimuthal direction. For certain operating conditions, the propagating direction of the wave switches randomly. The strong turbulent noise prevailing in gas turbine combustors is a source of random excitation for the thermoacoustic modes and can be the cause of these switching events. A low-order model is proposed to describe qualitatively this property of the dynamics of thermoacoustic azimuthal modes. [...]

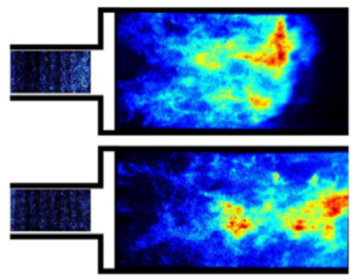
Investigation of thermoacoustic instability in sequential combustor during first stage lean blow-off
Y. Xiong, J. Droujko, O. Schulz and N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol. 38, 2021
The pressing need to increase the operational and fuel flexibility of gas turbines has recently led to the development of new combustor architectures such as constant-pressure-sequential-combustion systems. In this context, we investigated the thermoacoustic instabilities near the lean blow-off limit of the first stage in a generic sequential combustor. [...]

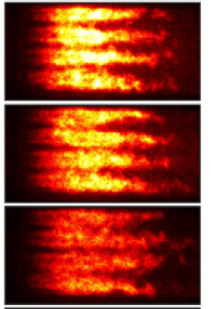
Linear and nonlinear entropy-wave response of technically-premixed jet-flames-array and swirled flame to acoustic forcing
M. Weilenmann, U. Doll, R. Bombach, A. Blondé, D. Ebi, Y. Xiong and N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol. 38, 2021
Broadband combustion noise is a major part of the total noise radiated by modern jet engines. It comprises two components: direct noise originating from the unsteady heat release of the flame, and indirect noise resulting from the acceleration of entropy fluctuations in the turbine stages. Not only do these entropy waves contribute to the noise pollution of aeroengines, they can also have a crucial role in the feedback loop leading to thermoacoustic instabilities, which induce vibrations and thermal loads that are highly detrimental for combustors and turbine components. This study presents quantitative measurements of the production of entropy waves in a technically premixed turbulent combustor, subject to acoustic forcing.[...]


Symmetry breaking of azimuthal waves: Slow-flow dynamics on the Bloch sphere
A. Faure-Beaulieu, N. Noiray
Physical Review Fluids, Vol. 5, 2020
Depending on the reflectional and rotational symmetries of annular combustors for aeroengines and gas turbines, self-sustained azimuthal thermoacoustic eigenmodes can be standing, spinning, or a mix of these two types of waves. These thermoacoustic limit cycles are unwanted because the resulting intense acoustic fields induce high-cycle fatigue of the combustor components. This paper presents a new theoretical framework for describing, in an idealized annular combustor, the dynamics of the slow-flow variables, which define the state of an eigenmode, i.e., if the latter is standing, spinning or mixed. [...]

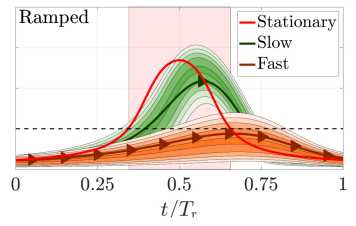
Bifurcation dodge: avoidance of a thermoacoustic instability under transient operation
G. Bonciolini, N. Noiray
Nonlinear Dynamics, Vol. 96, 2019
Varying one of the governing parameters of a dynamical system may lead to a critical transition, where the new stable state is undesirable. In some cases, there is only a limited range of the bifurcation parameter that corresponds to that unwanted attractor, while the system runs problem-less otherwise. In this study, we present experimental results regarding a thermoacoustic system subject to two consecutive and mirrored supercritical Hopf bifurcations [...]

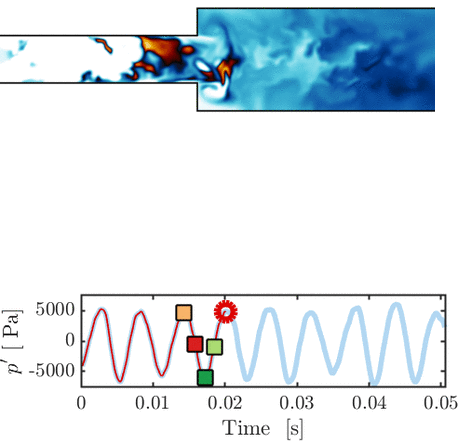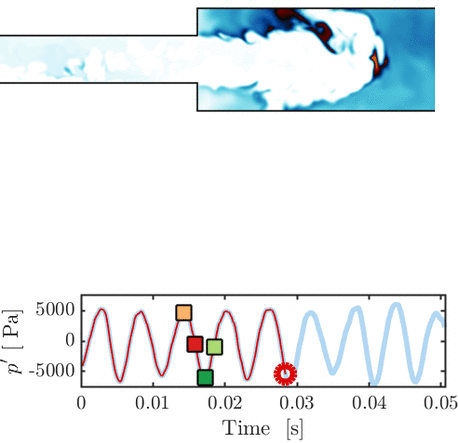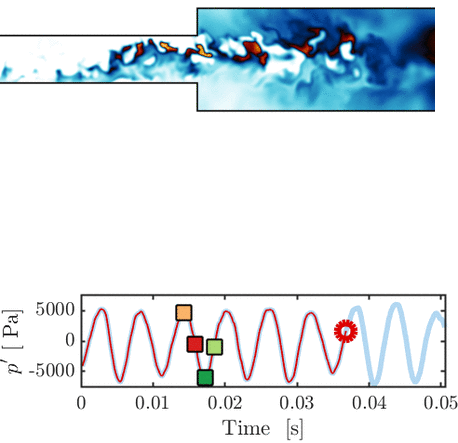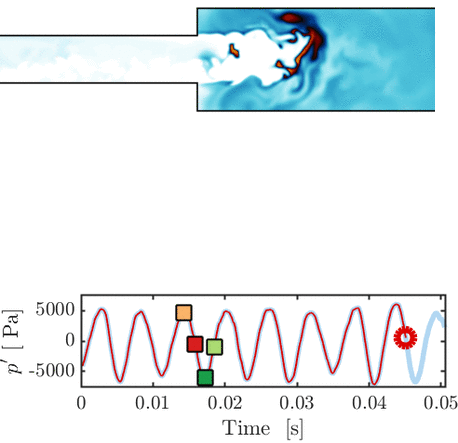
Thermoacoustic instability in a sequential combustor: Large eddy simulation and experiments
O. Schulz, U. Doll, D. Ebi, J. Droujko, C. Bourquard, N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol. 37, 2018
This paper presents a large eddy simulation (LES) of a generic sequential combustor (new class of combustors representing a major technology change for high operational flexibility with ultra-low NOx emissions) that features a thermoacoustic instability at 145 Hz. Both flames show strong oscillatory dynamics that are remarkably well captured by the LES. [...]

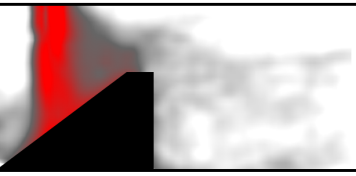
Background Oriented Schlieren of fuel jet flapping under thermoacoustic oscillations in a sequential combustor
M. Weilenmann, Y. Xiong, M. Bothien, N. Noiray
Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, Vol. 141, 2018
This study deals with thermoacoustic instabilities in a generic sequential combustor. The thermoacoustic feedback involves two flames: the perfectly premixed swirled flame anchored in the first stage and the sequential flame established downstream of the mixing section. It is shown that the large amplitude flapping of the secondary fuel jet in the mixing section plays a key role in the thermoacoustic feedback. [...]


Synchronization of Thermoacoustic Modes in Sequential Combustors
G. Bonciolini, N. Noiray
Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, Vol. 141, 2018
In this work, experimental data from our generic sequential combustor are presented, showing a particular bifurcation, where two thermoacoustic modes synchronize their self-sustained oscillations over a range of operating conditions. A low-order model of this thermoacoustic bifurcation is proposed. [...]

Effect of wall thermal inertia upon transient thermoacoustic dynamics of a swirl-stabilized flame
G. Bonciolini, D. Ebi, U. Doll, M. Weilenmann, N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol. 37, 2018
This study shows the importance of considering the thermal state of a combustor to investigate or predict its thermoacoustic stability. This aspect is often neglected or regarded as less important than the effect of the operating parameters, such as thermal power or equivalence ratio, but under certain circumstances it can have a dramatic influence on the development of the instabilities. [...]


Experiments and modelling of rate-dependent transition delay in a stochastic subcritical bifurcation
G. Bonciolini, D. Ebi, E. Boujo, N. Noiray
Royal Society Open Science, Vol. 5, 2018
In this publication, the effect of a continuous variation of a control parameter between two values corresponding to a stable and an unstable operation is assessed. This is particularly relevant for the development of combustors: operating conditions of gas turbines are often varied in time, for matching power grid requirement, and similar rapid changes of the combustion regimes also occur in aeronautical engines, especially at take-off. [...]

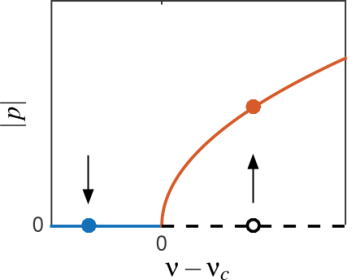
Flame Dynamics Intermittency in the Bistable Region Near a Subcritical Hopf Bifurcation
D. Ebi, A. Denisov, G. Bonciolini, E. Boujo and N. Noiray
Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, Vol. 140, 2018
We report experimental evidence of thermoacoustic bistability in a lab-scale turbulent combustor over a well-defined range of fuel–air equivalence ratios. Pressure oscillations are characterized by an intermittent behavior with “bursts,” i.e., sudden jumps between low and high amplitudes occurring at random time instants. [...]

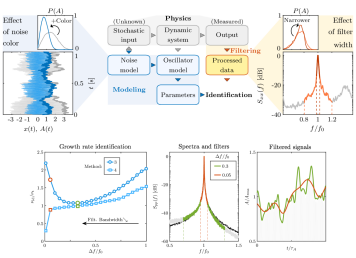
Output-only parameter identification of a colored-noise-driven Van der Pol oscillator - Thermoacoustic instabilities as an example
G. Bonciolini, E. Boujo and N. Noiray
Physical Review E, Vol. 95, 2017
The identification of the parameters of a thermoacoustic instability is an essential task in the design phase of a combustor. The identification relies on simplified models of the physics at play. In this paper we study the influence of the color of the turbulence-induced noise that forces the instability. In particular, we focus on the impact of the noise color on the accuracy of some output-only identification methods. The results can be also applied to any another nonlinear stochastic system driven by additive colored noise.
external page View at publisher
external page Pre-print version

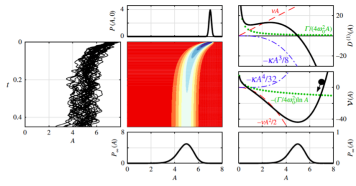
Robust identification of harmonic oscillator parameters using the adjoint Fokker–Planck equation
E. Boujo, N. Noiray
Proceedings of the Royal Society A, Vol. 473, 2017
In this paper, we improve the accuracy and robustness of output-only parameter identification in stochastic oscillators such as thermoacoustic systems. The method is based on the adjoint Fokker-Planck equation, which circumvents finite-time effects (associated with filtering, for instance). An iterative optimization procedure finds the optimal set of system parameters, given a model of the system and a single output measurement.
external page View at publisher
external page Pre-print version


Linear Growth Rate Estimation from Dynamics and Statistics of Acoustic Signal Envelope in Turbulent Combustors
N. Noiray
Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, Vol. 139, 2017
Considerable research and development efforts are required to meet the targets of future gas turbine technologies in terms of performance, emissions, and operational flexibility. One of the recurring problems is the constructive coupling between flames and combustor's acoustics. [...]


A method to identify thermoacoustic growth rates in combustion chambers from dynamic pressure time series
N. Noiray and A. Denisov
Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, Vol. 36, 2017
The stochastic nature of combustion instabilities in practical land-based gas turbines and aeroengines combustors has seldom been investigated. It is shown here that a wealth of information about the constructive acoustic-flame interactions can be gained by scrutinising the effects of the inherent turbulence-induced noise, which forces the nonlinear thermoacoustic dynamics. [...]

Quantifying acoustic damping using flame chemiluminescence
E. Boujo, A. Denisov, B. Schuermans and N. Noiray
Journal of Fluid Mechanics, Vol. 808, 2016
In this paper, we propose a new method for parameter identification in thermoacoustic systems, which we illustrate with measurements from a lab-scale combustion chamber. When signals of both acoustic pressure and flame OH* chemiluminescence are available, it is possible to reconstruct the acoustic-only linear transfer function. This allows us to identify separately the two components of the linear thermoacoustic growth rate: flame heat release and acoustic damping. We verify experimentally that the former depends on the fuel-air equivalence ratio while the latter is constant.
external page View at publisher
external page Pre-print version

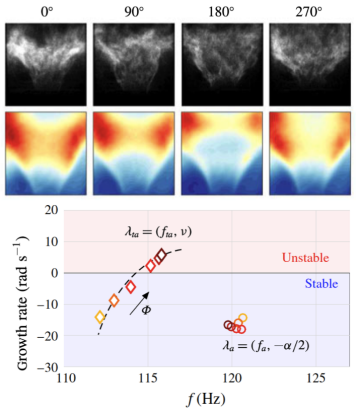
Analysis of Azimuthal Thermo-acoustic Modes in Annular Gas Turbine Combustion Chambers
M. R. Bothien, N. Noiray and B. Schuermans
Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2015
Modern gas turbine combustors operating in lean-premixed mode are prone to thermo-acoustic instabilities. In annular combustion chambers, usually azimuthal acoustic modes are the critical ones interacting with the flame. In case of constructive interference, high amplitude oscillations might result. In this paper, the azimuthal acoustic field of a full-scale engine is investigated in detail. [...]

Parametric system identification
On this topic:
Deterministic quantities characterizing noise driven Hopf bifurcations in gas turbine combustors
N. Noiray, B. Schuermans (2013)
external page International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics
Download Pre-print version (PDF, 547 KB)
Azimuthal thermoacoustic limit cycle

On this topic:
On the dynamic nature of azimuthal thermoacoustic modes in annular gas turbine combustion chambers
N. Noiray, B. Schuermans (2013)
external page Proceedings of the Royal Society A
Download Pre-print version (PDF, 1.3 MB)

